Description
The prehistoric predators may have had shaggy coats that changed colors with the seasons, helping them hunt.
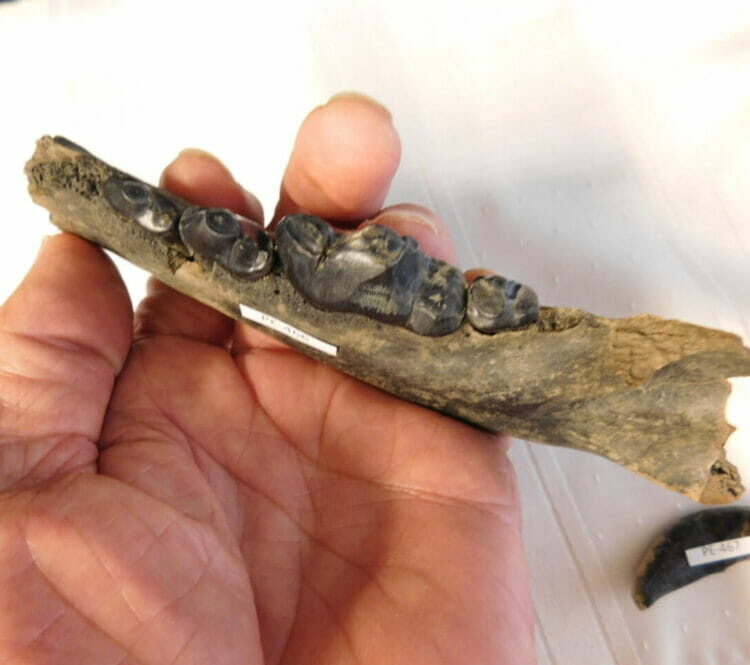
Hyenas originated in the jungles of Miocene Eurasia 22 million years ago, when most early feliform species were still largely arboreal. The first ancestral hyenas were likely similar to the modern African civet; one of the earliest hyena species described, Plioviverrops, was a lithe, civet-like animal that inhabited Eurasia 20–22 million years ago and is identifiable as a hyaenid by the structure of the middle ear and dentition. The lineage of Plioviverrops prospered and gave rise to descendants with longer legs and more pointed jaws, a direction similar to that taken by canids in North America. Hyenas then diversified into two distinct types: lightly built dog-like hyenas and robust bone-crushing hyenas. Although the dog-like hyenas thrived 15 million years ago (with one taxon having colonised North America), they became extinct after a change in climate, along with the arrival of canids into Eurasia. Of the dog-like hyena lineage, only the insectivorous aardwolf survived, while the bone-crushing hyenas (including the extant spotted, brown and striped hyenas) became the undisputed top scavengers of Eurasia and Africa